HEVC Encoder Optimization for HDR Video Coding Based on Perceptual Block Merging
Cheolkon Jung, Qiaozhou Lin, and Shengtao Yu
Xidian University
Abstract
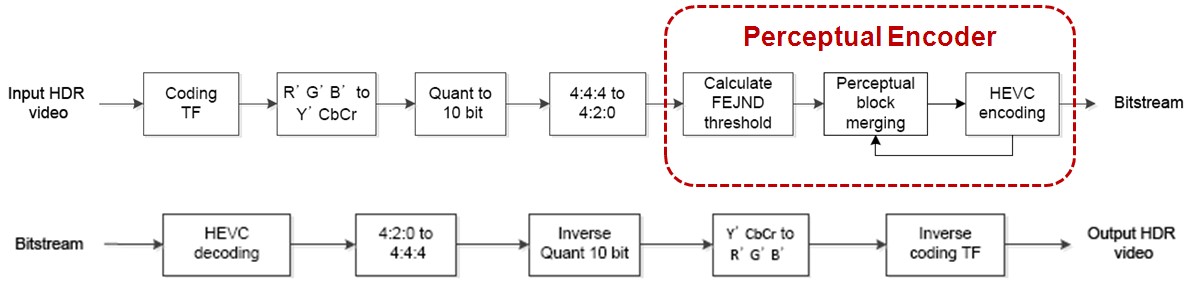
In this paper, we propose HEVC encoder optimization for HDR video coding based on perceptual block merging. We perform perceptual block merging for HEVC Main 10 Profile-based HDR video coding. First, we generate 10bit luminance adaptation (LA) for quantized HDR videos based on Barten contrast sensitivity function (CSF) model. Then, we obtain a free-energy based just-noticeable-difference (FEJND) map in each frame to represent the disorderly concealment effect. Next, we calculate average FEJND values of each coding unit (CU) and the frame from the FEJND map to get the perceptual Lagrange multiplier for rate-distortion optimization (RDO). Finally, we achieve perceptual block merging by minimizing RD costs based on the perceptual Lagrange multiplier. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method produces the block merging results more correlated with human visual perception, while successfully improving the visual quality of the reconstructed HDR videos.
Paper
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/VCIP.2016.7805536
Citation:
Cheolkon Jung, Qiaozhou Lin, and Shengtao Yu, "HEVC Encoder Optimization for HDR Video Coding Based on Perceptual Block Merging," in Proc. IEEE VCIP, 2016
Executable Files:
Results:
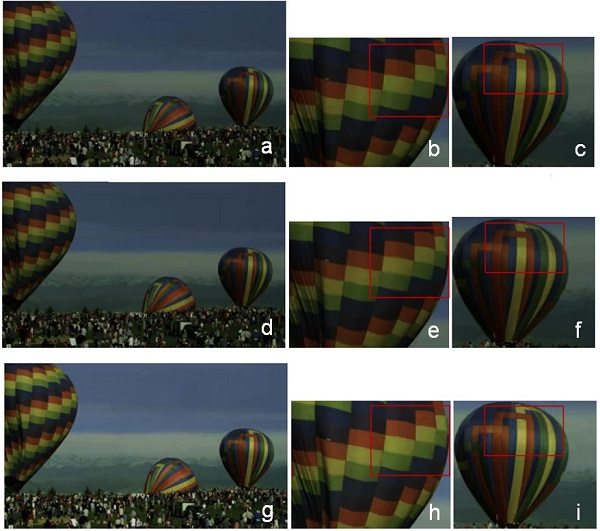

Fig. 1 Visual quality comparison in Balloon. (a) The reconstructed HDR frame by Anchor. (b), (c) Enlarged regions of (a). (d) The reconstructed HDR frame by [13]. (e), (f) Enlarged regions of (d). (g) The reconstructed HDR frame by the proposed method. (h), (i) Enlarged regions of (g).
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61271298) and the International S&T Cooperation Program of China (No. 2014DFG12780).